XL SPI1 BA
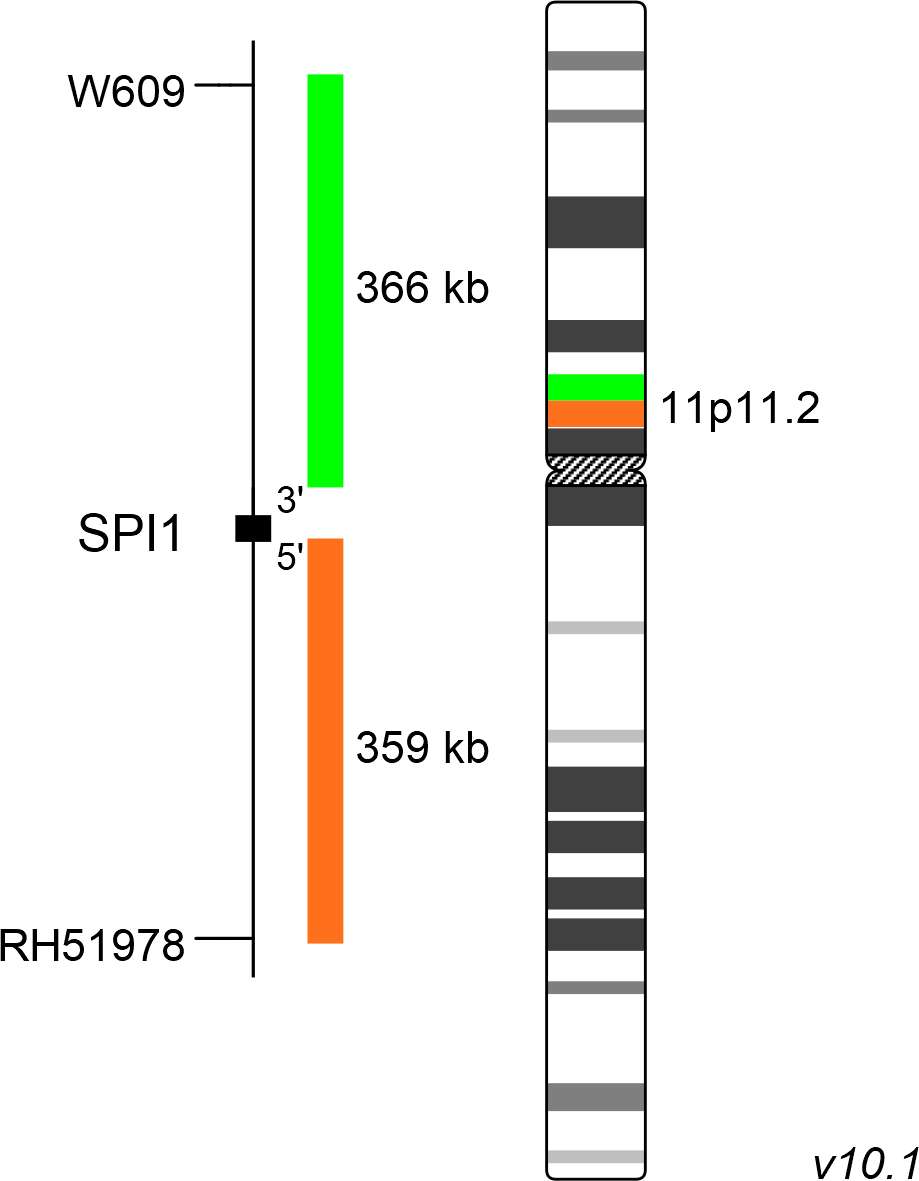
XL SPI1 BA is designed as a break apart probe. The orange labeled probe hybridizes proximal to the breakpoint in the SPI1 gene region at 11p11.2, the green labeled probe hybridizes distal to the breakpoint.
The SPI1 (SFFV provirus integration site-1) gene encodes the ETS-family transcription factor PU.1, which mediates gene expression during normal development of hematopoietic stem cells. SPI1 gene fusions were detected in 7 of 181 (3.9%) pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cases, analyzed and described by Seki et al. Genetic consequences of chromosomal rearrangements involving SPI1 are gene fusions containing 3\' exons of SPI1 and 5\' portions of TCF7, STMN1 and BCL11B. The cterminal DNA binding domain (ETS domain) of the PU.1 protein is present in all known fusions, irrespective of the fusion partner. Fusion-positive samples show strongly increased SPI1 expression levels, as the rearranged portion of SPI1 is placed under the control of heterologous promoters of the above-mentioned genes. As SPI1 is normally expressed as an early phase gene in T-cell development, expression of wildtype SPI1 or SPI1 fusion genes at later stages results in higher cell proliferation and differentiation/ maturation blockade during T-cell development. Fusion-positive cases show significantly shorter overall survival and are incurable when treated with standard chemotherapy.
SPI1 has recently been found to interact with the PML-RARα complex. Additionally, SPI1 itself is transcriptionally regulated by the PML-RARα fusion protein.
Cena za kus: pro registrované
The SPI1 (SFFV provirus integration site-1) gene encodes the ETS-family transcription factor PU.1, which mediates gene expression during normal development of hematopoietic stem cells. SPI1 gene fusions were detected in 7 of 181 (3.9%) pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cases, analyzed and described by Seki et al. Genetic consequences of chromosomal rearrangements involving SPI1 are gene fusions containing 3\' exons of SPI1 and 5\' portions of TCF7, STMN1 and BCL11B. The cterminal DNA binding domain (ETS domain) of the PU.1 protein is present in all known fusions, irrespective of the fusion partner. Fusion-positive samples show strongly increased SPI1 expression levels, as the rearranged portion of SPI1 is placed under the control of heterologous promoters of the above-mentioned genes. As SPI1 is normally expressed as an early phase gene in T-cell development, expression of wildtype SPI1 or SPI1 fusion genes at later stages results in higher cell proliferation and differentiation/ maturation blockade during T-cell development. Fusion-positive cases show significantly shorter overall survival and are incurable when treated with standard chemotherapy.
SPI1 has recently been found to interact with the PML-RARα complex. Additionally, SPI1 itself is transcriptionally regulated by the PML-RARα fusion protein.
Cena za kus: pro registrované




